ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2023; 7(4):380-392. doi:10.7150/ntno.79187 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Peelable Microneedle Patches Deliver Fibroblast Growth Factors to Repair Skin Photoaging Damage
1. Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union of Medical College, 33 Ba-Da-Chu Rd., Beijing, 100144, P.R. China.
2. Department of Molecular Biomedical Sciences and Comparative Medicine Institute, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 27607, United States.
3. Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, United States, and North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 27606, United States.
Abstract
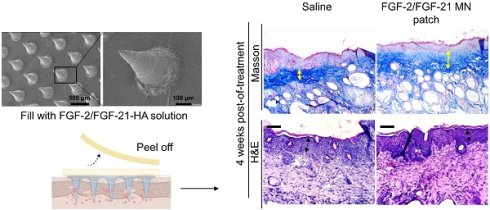
Rationale: UV light deeply penetrates the dermis, leading to inflammation and cell death with prolonged exposure. This is a major contributor to skin photoaging. In the pharmaceutical field, fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) have gained popularity for enhancing skin quality as they facilitate tissue remodeling and re-epithelization. Nonetheless, their effectiveness is significantly hindered by limited absorption.
Methods: We have successfully created a dissolving microneedle (MN) patch that contains hyaluronic acid (HA) loaded with FGF-2 and FGF-21. This patch aims to improve the therapeutic efficiency of these growth factors while providing a simple administration method. We determined the performance of this patch in an animal model of skin photoaging.
Results: The FGF-2/FGF-21-loaded MN (FGF-2/FGF-21 MN) patch demonstrated a consistent structure and suitable mechanical properties, allowing for easy insertion and penetration into mouse skin. Within 10 minutes of application, the patch released approximately 38.50 ± 13.38% of the loaded drug. Notably, the FGF-2/FGF-21 MNs exhibited significant improvements in UV-induced acute skin inflammation and reduced mouse skin wrinkles within a span of two weeks. Furthermore, the positive effects continued to enhance over a four-week treatment period.
Conclusion: The proposed HA-based peelable MN patch provides an efficient approach for transdermal drug delivery, providing a promising method for improved therapeutic outcomes.
Keywords: microneedles, transdermal delivery, hyaluronic acid, photoaging, UV, fibroblast growth factors

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact