ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2021; 5(1):27-35. doi:10.7150/ntno.51391 This issue Cite
Review
Imaging of cell-based therapy using 89Zr-oxine ex vivo cell labeling for positron emission tomography
Molecular Imaging Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA
Abstract
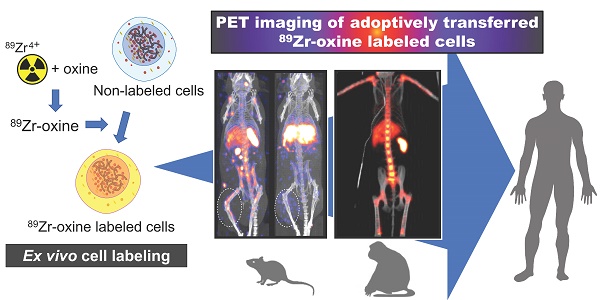
With the rapid development of anti-cancer cell-based therapies, such as adoptive T cell therapies using tumor-infiltrating T cells, T cell receptor transduced T cells, and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there has been a growing interest in imaging technologies to non-invasively track transferred cells in vivo. Cell tracking using ex vivo cell labeling with positron emitting radioisotopes for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging has potential advantages over single-photon emitting radioisotopes. These advantages include intrinsically higher resolution, higher sensitivity, and higher signal-to-background ratios. Here, we review the current status of recently developed Zirconium-89 (89Zr)-oxine ex vivo cell labeling with PET imaging focusing on its applications and future perspectives. Labeling of cells with 89Zr-oxine is completed in a series of relatively simple steps, and its low radioactivity doses required for imaging does not interfere with the proliferation or function of the labeled immune cells. Preclinical studies have revealed that 89Zr-oxine PET allows high-resolution in vivo tracking of labeled cells for 1-2 weeks after cell transfer both in mice and non-human primates. These results provide a strong rationale for the clinical translation of 89Zr-oxine PET-based imaging of cell-based therapy.
Keywords: Zirconium-89, Zirconium-89 oxine, cell tracking, positron emission tomography, cell-based therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact