ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2022; 6(4):436-450. doi:10.7150/ntno.73918 This issue Cite
Review
Progress on Applying Carbon Dots for Inhibition of RNA Virus Infection
1. Department of Chemistry, Pakokku University, Myaing Road, Pakokku 90401, Myanmar.
2. Department of Chemistry, University of Miami, Coral Gables, FL 33146, USA.
3. Department of Chemistry, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya 60115, Indonesia.
4. Supramodification Nano-micro Engineering Research Group, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya 60115, Indonesia.
5. Research Director at Walchand Center for Research in Nanotechnology and Bionanotechnology, Walchand College of Arts and Science, W. H. Road, Ashok Chowk, Solapur 413006, India.
Abstract
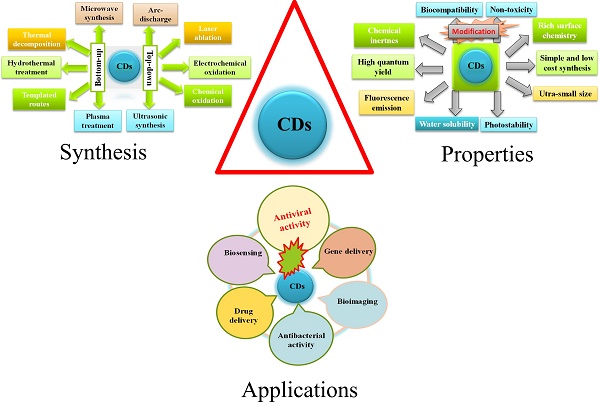
Viral infection is a globally leading health issue. Annually, new lethal RNA viruses unexpectedly emerged and mutated threatening health and safety. Meanwhile, it is urgent to explore novel antiviral agents, which, however, takes years to be clinically available. Nonetheless, the development of carbon dots (CDs) in the past 20 years has exhibited their vast application potentials and revealed their promising capacity as future antiviral agents considering their versatile properties and significant antiviral responses. Thus, CDs have been widely investigated as an alternative of traditional chemotherapy for inhibiting viral infection and replication in vitro. Meanwhile, attempts to apply CDs to in vivo systems are in high demand. In this review, recent developments of CDs-based antiviral therapies are systematically summarized. Furthermore, the role of CDs in photodynamic inactivation to kill viruses or bacteria is briefly discussed.
Keywords: RNA virus, virus infection treatment, carbon dots, nanomedicine, antiviral therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact