ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2022; 6(2):215-229. doi:10.7150/ntno.62351 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Lipid nitroalkene nanoparticles for the focal treatment of ischemia reperfusion
1. Center for Ultrasound Molecular Imaging and Therapeutics, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA;
2. Department of Pharmacology and Chemical Biology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.
Abstract
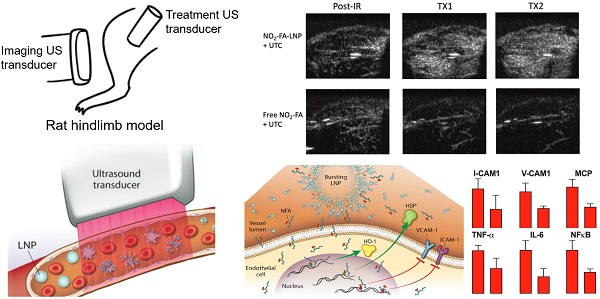
Rationale: The treatment of microvascular obstruction (MVO) using ultrasound-targeted LNP cavitation (UTC) therapy mechanically relieves the physical obstruction in the microcirculation but does not specifically target the associated inflammatory milieu. Electrophilic fatty acid nitroalkene derivatives (nitro-fatty acids), that display pleiotropic anti-inflammatory signaling and transcriptional regulatory actions, offer strong therapeutic potential but lack a means of rapid targeted delivery. The objective of this study was to develop nitro-fatty acid-containing lipid nanoparticles (LNP) that retain the mechanical efficacy of standard LNP and can rapidly target delivery of a tissue-protective payload that reduces inflammation and improves vascular function following ischemia-reperfusion.
Methods: The stability and acoustic behavior of nitro-fatty acid LNP (NO2-FA-LNP) were characterized by HPLC-MS/MS and ultra-high-speed microscopy. The LNP were then used in a rat hindlimb model of ischemia-reperfusion injury with ultrasound-targeted cavitation.
Results: Intravenous administration of NO2-FA-LNP followed by ultrasound-targeted LNP cavitation (UTC) in both healthy rat hindlimb and following ischemia-reperfusion injury showed enhanced NO2-FA tissue delivery and microvascular perfusion. In addition, vascular inflammatory mediator expression and lipid peroxidation were decreased in tissues following ischemia-reperfusion revealed NO2-FA-LNP protected against inflammatory injury.
Conclusions: Vascular targeting of NO2-FA-LNP with UTC offers a rapid method of focal anti-inflammatory therapy at sites of ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Keywords: ultrasound-targeted lipid nanoparticle cavitation, microvascular obstruction, acute myocardial infarction, inflammation, nitro-fatty acid, nitroalkene

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact