ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2022; 6(2):126-142. doi:10.7150/ntno.63158 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dendrimer-2PMPA selectively blocks upregulated microglial GCPII activity and improves cognition in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis
1. Johns Hopkins Drug Discovery, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
2. Center for Nanomedicine, Department of Ophthalmology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
3. Department of Neurology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
4. Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
5. Department of Pharmacology and Molecular Sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
6. Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
7. Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
8. Kennedy Krieger Institute, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
9. Department of Neuroscience, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
10. Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
11. Department of Oncology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
*Authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
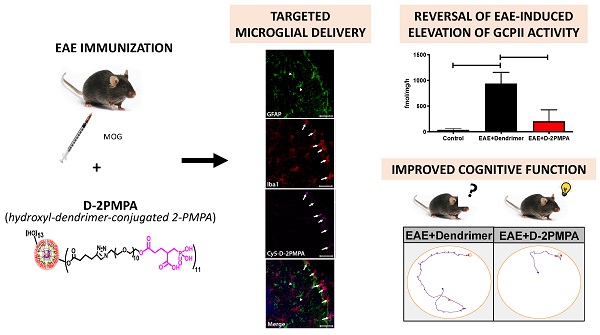
Cognitive impairment is a common aspect of multiple sclerosis (MS) for which there are no treatments. Reduced brain N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) levels are linked to impaired cognition in various neurological diseases, including MS. NAAG levels are regulated by glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII), which hydrolyzes the neuropeptide to N-acetyl-aspartate and glutamate. GCPII activity is upregulated multifold in microglia following neuroinflammation. Although several GCPII inhibitors, such as 2-PMPA, elevate brain NAAG levels and restore cognitive function in preclinical studies when given at high systemic doses or via direct brain injection, none are clinically available due to poor bioavailability and limited brain penetration. Hydroxyl-dendrimers have been successfully used to selectively deliver drugs to activated glia.
Methods: We attached 2-PMPA to hydroxyl polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers (D-2PMPA) using a click chemistry approach. Cy5-labelled-D-2PMPA was used to visualize selective glial uptake in vitro and in vivo. D-2PMPA was evaluated for anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-treated glial cultures. In experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)-immunized mice, D-2PMPA was dosed biweekly starting at disease onset and cognition was assessed using the Barnes maze, and GCPII activity was measured in CD11b+ hippocampal cells.
Results: D-2PMPA showed preferential uptake into microglia and robust anti-inflammatory activity, including elevations in NAAG, TGFβ, and mGluR3 in glial cultures. D-2PMPA significantly improved cognition in EAE mice, even though physical severity was unaffected. GCPII activity increased >20-fold in CD11b+ cells from EAE mice, which was significantly mitigated by D-2PMPA treatment.
Conclusions: Hydroxyl dendrimers facilitate targeted drug delivery to activated microglia. These data support further development of D-2PMPA to attenuate elevated microglial GCPII activity and treat cognitive impairment in MS.
Keywords: multiple sclerosis, cognitive impairment, dendrimer, GCPII, NAAG

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact