ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2021; 5(4):431-444. doi:10.7150/ntno.55165 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tracking adoptive T cell immunotherapy using magnetic particle imaging
1. J Crayton Pruitt Family Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL USA.
2. Preston A. Wells, Jr. Center for Brain Tumor Therapy, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL USA.
3. Lillian S. Wells Department of Neurosurgery, McKnight Brain Institute, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL USA.
4. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL USA.
5. UF Health Cancer Center, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL USA.
Abstract
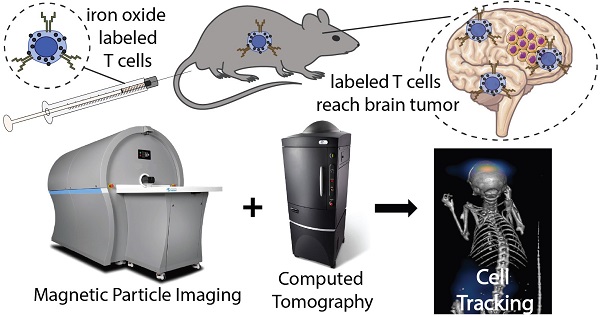
Adoptive cellular therapy (ACT) is a potent strategy to boost the immune response against cancer. ACT is effective against blood cancers but faces challenges in treating solid tumors. A critical step for the success of ACT immunotherapy is to achieve efficient trafficking and persistence of T cells to solid tumors. Non-invasive tracking of the accumulation of adoptively transferred T cells to tumors would greatly accelerate development of more effective ACT strategies. We demonstrate the use of magnetic particle imaging (MPI) to non-invasively track ACT T cells in vivo in a mouse model of brain cancer. Magnetic labeling did not impair primary tumor-specific T cells in vitro, and MPI allowed the detection of labeled T cells in the brain after intravenous or intracerebroventricular administration. These results support the use of MPI to track adoptively transferred T cells and accelerate the development of ACT treatments for brain tumors and other cancers.
Keywords: biomedical imaging, brain cancer, cell labeling, cellular therapy, iron oxide nanoparticles

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact