ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2020; 4(1):40-56. doi:10.7150/ntno.37738 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Phospholipid prodrug conjugates of insoluble chemotherapeutic agents for ultrasound targeted drug delivery
1. Departments of Chemistry, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, 801 Leroy Place, Socorro, NM 87801, USA
2. Materials Engineering, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, 801 Leroy Place, Socorro, NM 87801, USA
3. Chemical Engineering, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, 801 Leroy Place, Socorro, NM 87801, USA
Abstract
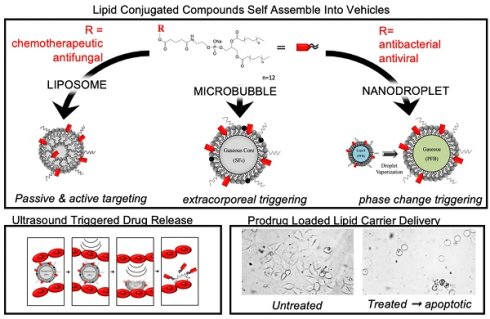
The hydrophobicity and high potency of many therapeutic agents makes them difficult to use effectively in clinical practice. This work focuses on conjugating phospholipid tails (2T) onto podophyllotoxin (P) and its analogue (N) using a linker and characterizing the effects of their incorporation into lipid-based drug delivery vehicles for triggered ultrasound delivery. Differential Scanning Calorimetry results show that successfully synthesized lipophilic prodrugs, 2T-P (~28 % yield) and 2T-N(~26 % yield), incorporate within the lipid membranes of liposomes. As a result of this, increased stability and incorporation are observed in 2T-P and 2T-N in comparison to the parent compounds P and N. Molecular dynamic simulation results support that prodrugs remain within the lipid membrane over a relevant range of concentrations. 2T-N's (IC50: 20 nM) biological activity was retained in HeLa cells (cervical cancer), whereas 2T-P's (IC50: ~4 µM) suffered, presumably due to steric hindrance. Proof-of-concept studies using ultrasound in vitro microbubble and nanodroplet delivery vehicles establish that these prodrugs are capable of localized drug delivery. This study provides useful information about the synthesis of double tail analogues of insoluble chemotherapeutic agents to facilitate incorporation into drug delivery vehicles. The phospholipid attachment strategy presented here could be applied to other well suited drugs such as gemcitabine, commonly known for its treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: prodrug-loaded liposomes, podophyllotoxin, microbubbles, ultrasound, lipid, targeted drug delivery

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact