ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2017; 1(4):389-402. doi:10.7150/ntno.21268 This issue Cite
Review
Nanomaterial-based Microfluidic Chips for the Capture and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells
1. Institute of Medical Instrument and Application, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510006, P. R. China;
2. Department of Immunology, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, P. R. China.
Abstract
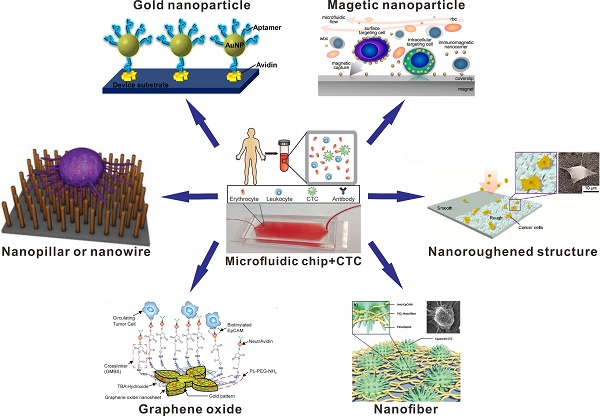
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs), a type of cancer cells that spreads from primary or metastatic tumors into the bloodstream, can lead to a new fatal metastasis. As a new type of liquid biopsy, CTCs have become a hot pursuit and detection of CTCs offers the possibility for early diagnosis of cancers, earlier evaluation of chemotherapeutic efficacy and cancer recurrence, and choice of individual sensitive anti-cancer drugs. The fundamental challenges of capturing and characterizing CTCs are the extremely low number of CTCs in the blood and the intrinsic heterogeneity of CTCs. A series of microfluidic devices have been proposed for the analysis of CTCs with automation capability, precise flow behaviors, and significant advantages over the conventional larger scale systems. This review aims to provide in-depth insights into CTCs analysis, including various nanomaterial-based microfluidic chips for the capture and detection of CTCs based on the specific biochemical and physical properties of CTCs. The current developmental trends and promising research directions in the establishment of microfluidic chips for the capture and detection of CTCs are also discussed.
Keywords: circulating tumor cells, nanomaterial, microfluidic chips, cancer.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact