ISSN: 2206-7418Nanotheranostics
Nanotheranostics 2020; 4(1):1-13. doi:10.7150/ntno.39810 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Thermo-responsive Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging and Treatment of Cancers
1. Department of Bioengineering, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX 76019, USA
2. Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX 75390, USA
3. Department of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI 02881, USA
4. Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX 75390, USA
5. Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX 75390, USA
6. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA
7. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21201, USA
8. Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21201, USA
Abstract
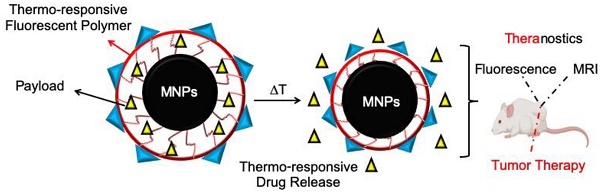
Theranostic systems capable of delivering imaging and therapeutic agents at a specific target are the focus of intense research efforts in drug delivery. To overcome non-degradability and toxicity concerns of conventional theranostic systems, we formulated a novel thermo-responsive fluorescent polymer (TFP) and conjugated it on the surface of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) for imaging and therapeutic applications in solid tumors. Methods: TFP-MNPs were synthesized by copolymerizing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), allylamine and a biodegradable photoluminescent polymer, and conjugating it on MNPs via a free radical polymerization reaction. Physicochemical properties of the nanoparticles were characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering, and vibrational sample magnetometry. Nanoparticle cytocompatibility, cellular uptake and cytotoxicity were evaluated using in vitro cell assays. Finally, in vivo imaging and therapeutic efficacy studies were performed in subcutaneous tumor xenograft mouse models. Results: TFP-MNPs of ~135 nm diameter and -31 mV ζ potential maintained colloidal stability and superparamagnetic properties. The TFP shell was thermo-responsive, fluorescent, degradable, and released doxorubicin in response to temperature changes. In vitro cell studies showed that TFP-MNPs were compatible to human dermal fibroblasts and prostate epithelial cells. These nanoparticles were also taken up by prostate and skin cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner and exhibited enhanced killing of tumor cells at 41°C. Preliminary in vivo studies showed theranostic capabilities of the nanoparticles with bright fluorescence, MRI signal, and therapeutic efficacy under magnetic targeting after systemic administration in tumor bearing mice. Conclusion: These results indicate the potential of TFP-MNPs as multifunctional theranostic nanoparticles for various biological applications, including solid cancer management.
Keywords: theranostic systems, thermo-responsive polymers, photoluminescent polymers, solid tumors, magnetic nanoparticles
